What Is The Normal Balance Of Dividends

He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. Each account can be represented visually by splitting the account into left and right sides as shown. This graphic representation of a general ledger account is known as a T-account. A T-account is called a “T-account” because it looks like a “T,” as you can see with the T-account shown here. We want to specifically keep track of Dividends in a separate account so we assign it a Normal Debit Balance.
What Is The Normal Balance Of Dividends
- Understanding the normal balance of dividends is a fundamental aspect of financial management and contributes to the overall success and stability of a company.
- The normal balance refers to the side of the general ledger account where increases are recorded.
- This involves knowing the concept of a “normal balance,” which dictates how increases and decreases are posted to different types of accounts within an accounting system.
- They are not considered an operating expense, unlike costs such as salaries or rent.
- When it comes to dividends, the normal balance is typically on the debit side of the ledger.
- Let’s say there were a credit of $4,000 and a debit of $6,000 in the Accounts Payable account.
Accounts Payable is a liability account, and thus its what is the normal balance of dividends normal balance is a credit. In summary, the normal balance of dividends is typically on the debit side of the ledger. Understanding the normal balance of an account is crucial for accurate financial record-keeping. By ensuring that the correct side of the ledger is debited or credited for dividends, accountants can provide reliable financial statements that reflect the company’s financial health. Accounting software often includes controls to prevent errors when recording transactions, further safeguarding the integrity of financial records. Now the question is that on which side the increase or decrease in an account is to be recorded.
How to Calculate APIC (Additional Paid-in Capital)
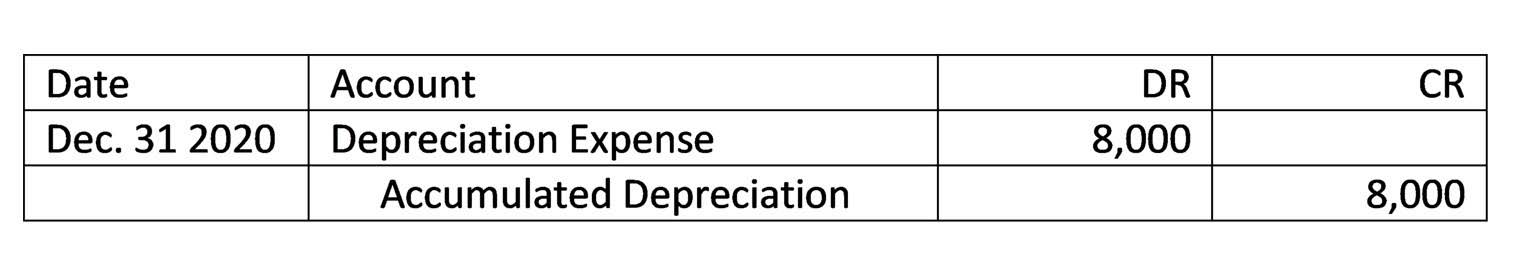
So for example there are contra expense accounts such as purchase returns, contra revenue accounts such as sales returns and contra asset accounts such as accumulated depreciation. Welcome to the world of finance, where understanding the nuances of various accounting concepts is essential. One such concept is dividends, which play a crucial role in the financial landscape. Dividends are the returns that a company distributes to its shareholders Online Accounting as a reward for their investment.
- The normal account balance is nothing but the expectation that the specific account is debit or credit.
- By ensuring that the correct side of the ledger is debited or credited for dividends, accountants can provide reliable and meaningful financial statements.
- In Example 1, where a cash dividend is paid, the debit entry is recorded under Dividends Payable, reflecting the reduction in the company’s retained earnings.
- Because of the impact on Equity (it decreases), we assign a Normal Debit Balance.
- Factors such as company structure, profitability, legal requirements, investor expectations, and business strategy can influence the normal balance of dividends.
- In each of these examples, the normal balance of dividends varies based on the specific circumstances.
Normal Balances in Accounting

In the world of accounting, the concept of normal balance refers to the side of the general ledger account where increases are recorded. Each account in the financial records has a normal balance, which is determined by its nature and function. Understanding the normal balance of an account is crucial for accurately recording and summarizing financial transactions.

This becomes easier to understand as you become familiar with the normal balance of an account. It should be noted that if an account is normally a debit balance it is increased by a debit entry, and if an account is normally a credit balance it is increased by a credit entry. So for example a debit entry to an asset account will increase the asset balance, and a credit entry to a liability account will increase the liability. Each of the accounts https://thebarbercompany.es/lower-taxes-for-independent-contractors-and/ in a trial balance extracted from the bookkeeping ledgers will either show a debit or a credit balance. The normal balance of any account is the balance (debit or credit) which you would expect the account have, and is governed by the accounting equation. Asset accounts, such as Cash or Accounts Receivable, and Expense accounts increase with a debit entry.
It is always recommended to consult the specific accounting guidelines and policies applicable to the organization in question. For reference, the chart below sets out the type, side of the accounting equation (AE), and the normal balance of some typical accounts found within a small business bookkeeping system. Since dividend payments are a reduction of retained earnings for an entity it has a debit balance as its reduction of share holder’s equity. Modern tools like QuickBooks, Xero, NetSuite, Bench, Pilot, and FreshBooks make it easier to keep track of account balances.

They follow the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), making tasks simpler and more reliable. When we’re talking about Normal Balances for Revenue accounts, we assign a Normal Balance based on the effect on Equity. Because of the impact on Equity (it increases), we assign a Normal Credit Balance.
Leave a Reply